Presenting my work on power dynamics in digital planning and co-organizing a workshop on Urban AI at CUPUM 2025 in London.
Jun 30, 2025
Presented and co-organized the international conference CPCB 2025 at Utrecht University, focusing on digital participation and power in planning.
May 5, 2025
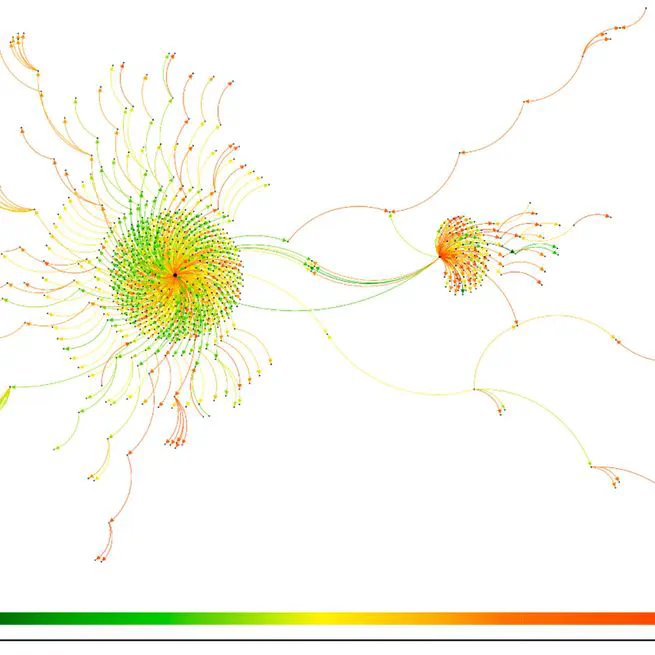
Power relation study by Social Network Analysis
Sep 16, 2024

Empowering grassroots in urban planning through social media
Aug 27, 2024
Our latest article explores citizens’ affective perception and cognitive learning of urban planning elements in Cities: Skylines online communities through social media data analytics.
Aug 1, 2024

Guest lecture on using social media data for urban planning.
Jan 15, 2024
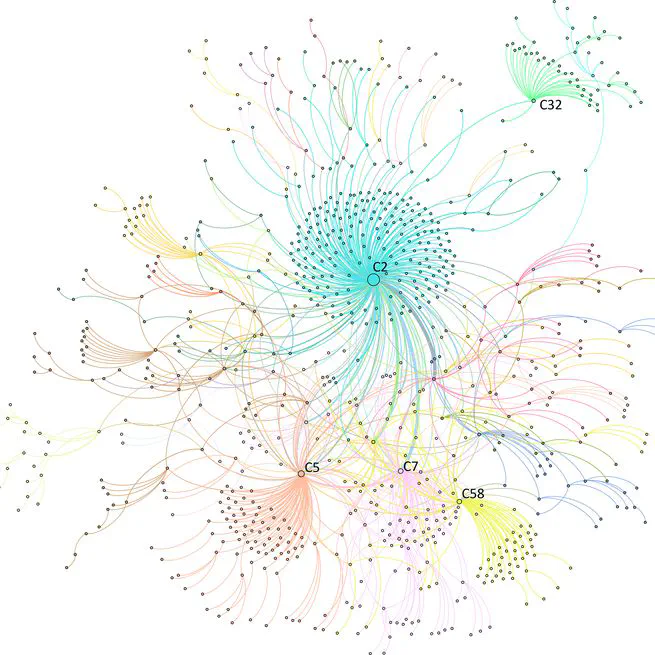
Unequal power relations in online planning controversy
Jan 1, 2024
Presented research on the role of social media in analyzing power relations at CUPUM 2023, the 18th International Conference on Computational Urban Planning and Urban Management.
Jul 15, 2023

Journalists and civil society organizations use social media to challenge planning decisions.
Jun 13, 2023
Co-supervision for Yujian Qiu's research on citizen perceptions of urban planning using data from a city simulation game.
Jan 1, 2023